Passenger kilometer is a unit of measurement that is equivalent to transporting one passenger over a distance of one kilometer.
Industry Business Model
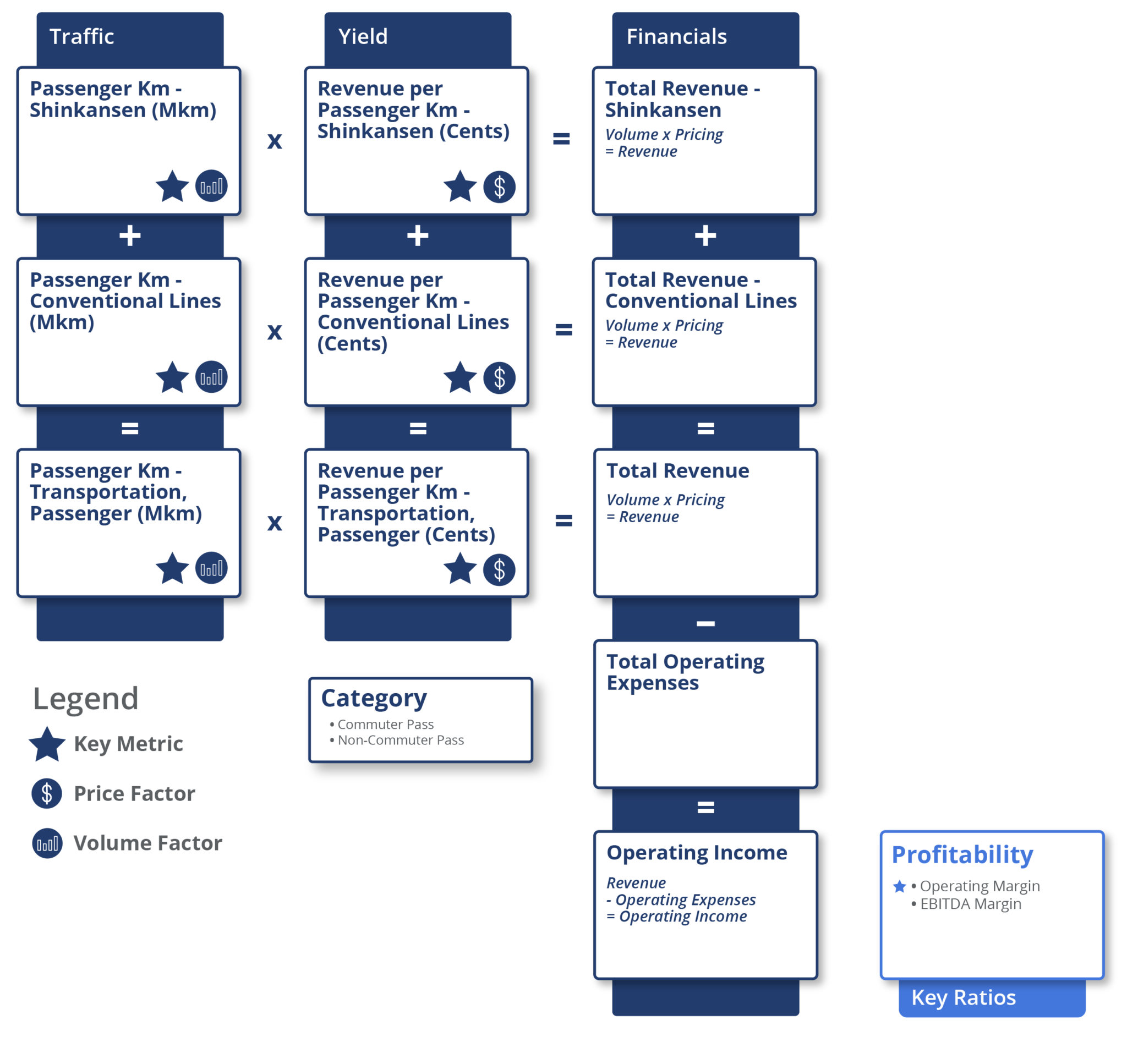
The business model of the Japanese passenger railroad industry is fairly straightforward. Companies in the passenger railroad industry generate revenue by charging a travel fare to passengers for the transit services rendered. These companies also determine the prices of passenger fares, however, these fares are regulated by Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism.
REVENUE ANALYSIS
Companies in the passenger railroad industry use the following metrics to compute revenue:
- Passenger kilometers; and
- Revenue per passenger kilometer
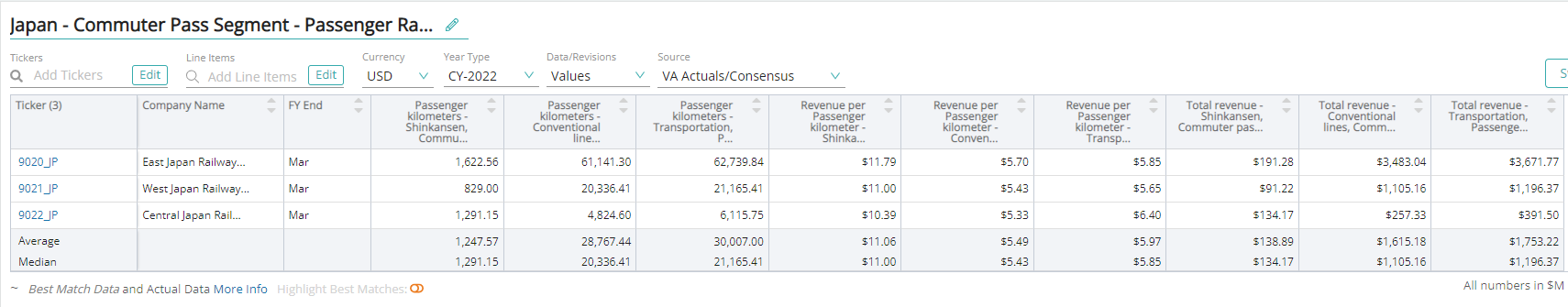
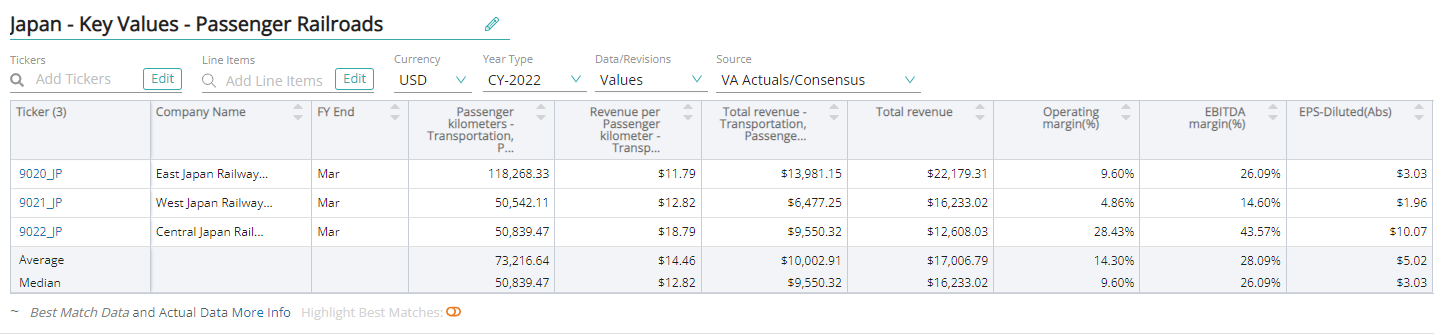
To calculate revenue, analysts multiply passenger-kilometers with revenue per passenger kilometer, for the particular type of rail network used. This calculation is done separately for the network of railway lines used, commuter pass and non-commuter pass and eventually summed together to arrive at total revenue.
Passenger kilometers are a measure of the movement of passengers over the distance traveled. It is calculated as total passengers carried (number) multiplied by the total distance traveled (km). Revenue per passenger kilometer is the fare charged to a passenger for every kilometer traveled.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the most important business metrics for a particular industry. When understanding market expectations for passenger railroads, whether at a company or industry level, some passenger railroads KPIs to consider include:
Visible Alpha’s Standardized Industry Metrics
To understand market expectations for the passenger railroads industry, a key information source is sell-side analyst estimate and consensus forecast data. The buy-side, sell-side, and public companies leverage this type of data to conduct competitive analysis, a type of analysis conducted by professional analysts that involves comparing standardized metrics of one company with those of similar companies. Because companies report metrics differently – and sometimes report on different metrics altogether – standardizing the key metrics for each company can be a cumbersome process.
Visible Alpha Insights includes analyst data, company data, and industry data at a level of granularity unparalleled in the market. Our industry data – Standardized Industry Metrics – enables market participants to quantify and compare market expectations for companies across 150+ industries.
Data as of January 2023
Industry KPI Terms & Definitions
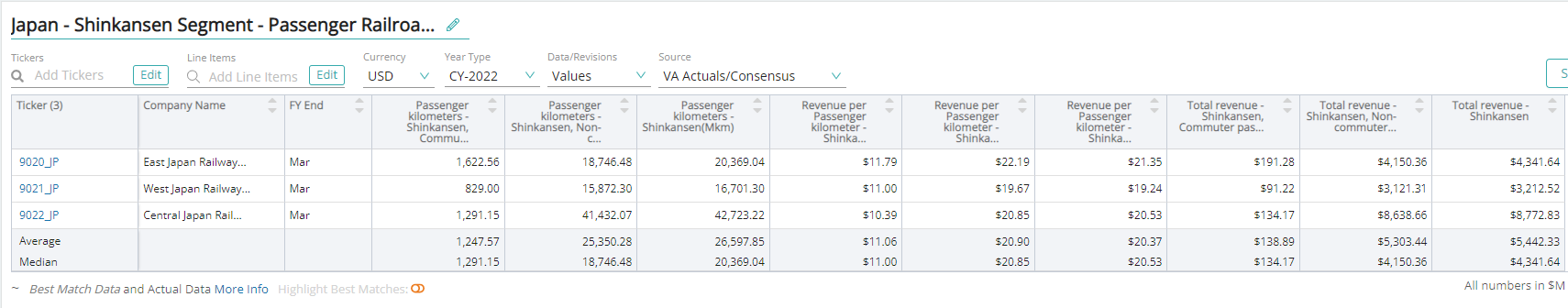
Shinkansen
Shinkansen is Japanese for bullet train, which is a high-speed intercity rail system operated in Japan by JR East, JR Central, JR West, and JR Kyushu. Shinkansen is a long-distance intercity train service and hence has fewer stations than conventional railway lines.
The train does not share its tracks with other conventional trains because the rail gauge of the Shinkansen is much wider at 1.435 meters. Shinkansen trains run at a speed of ~200–250 km/h. The fare systems applied to the Shinkansen and conventional rails are different.
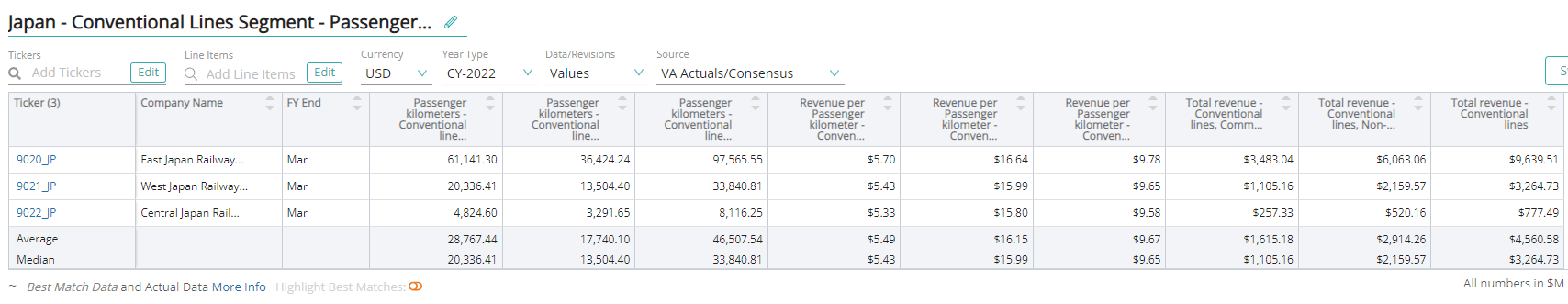
Conventional
Conventional rail is a relatively slow-speed rail system that runs on conventional rail tracks at a maximum speed of 160 km/h.
Commuter Pass
Commuter pass is a credit card-sized railway pass that is either magnetically encoded or contains an integrated circuit (IC) chip. The pass allows passengers to travel between specified stations, for a period of one, three, or six months. The commuter pass is comparatively cheaper than a normal ticket fare.
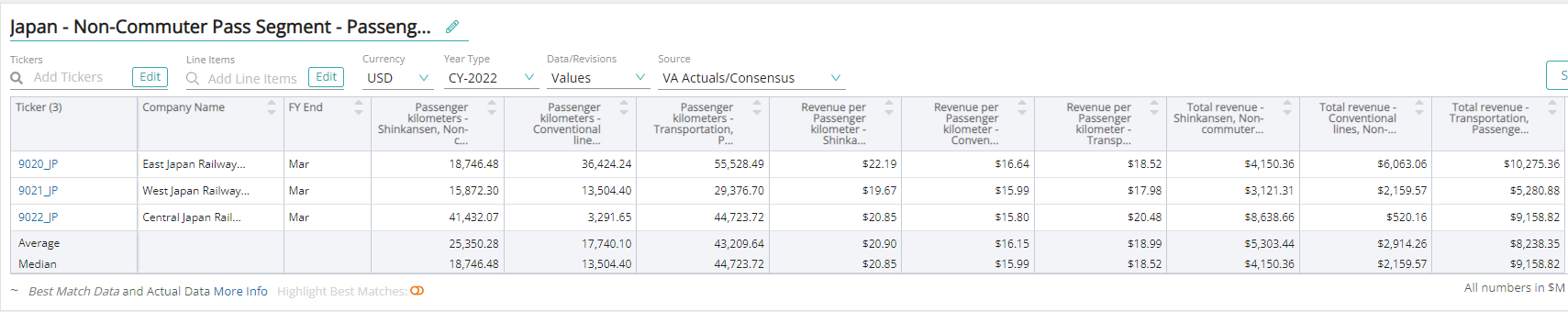
Non-commuter Pass
Non-commuter pass is a one-way railway ticket used by passengers who aren’t regular commuters, to travel by train.
Passenger Kilometers
Passenger kilometer is a unit of measurement that is equivalent to transporting one passenger over a distance of one kilometer.
Revenue Per Passenger Kilometers
Revenue per passenger kilometers (RPK) (or revenue per passenger miles (RPM) when the measurement unit is in miles) is an industry metric that shows the number of kilometers traveled by a paying passenger. It is calculated as the number of revenue passengers multiplied by the total distance traveled.
Passenger Kilometers – Shinkansen
Passenger kilometer – Shinkansen is a unit of measurement that is equivalent to transporting one passenger over a distance of one kilometer by a Shinkansen train.
Passenger Kilometers – Conventional
Passenger kilometer – conventional is a unit of measurement that is equivalent to transporting one passenger over a distance of one kilometer by a conventional train.
Revenue Per Passenger Kilometers – Shinkansen
Revenue per passenger kilometers (RPK) – Shinkansen is an industry metric that shows the number of kilometers traveled by a paying passenger. It is calculated as the number of revenue passengers multiplied by the total distance traveled by a Shinkansen train.
Revenue Per Passenger Kilometers – Conventional
Revenue per passenger kilometers (RPK) – conventional is an industry metric that shows the number of kilometers traveled by a paying passenger. It is calculated as the number of revenue passengers multiplied by the total distance traveled by a conventional train.
Download this guide as an ebook today:
Guide to Passenger Railroad KPIs for Investment Professionals
This guide highlights the key performance indicators for the passenger railroad industry and where investors should look to find an investment edge, including:
- Passenger Railroad Business Model & Diagram
- Key Passenger Railroad Metrics PLUS Visible Alpha’s Standardized Industry Metrics
- Available Comp Tables
- Industry KPI Terms & Definitions