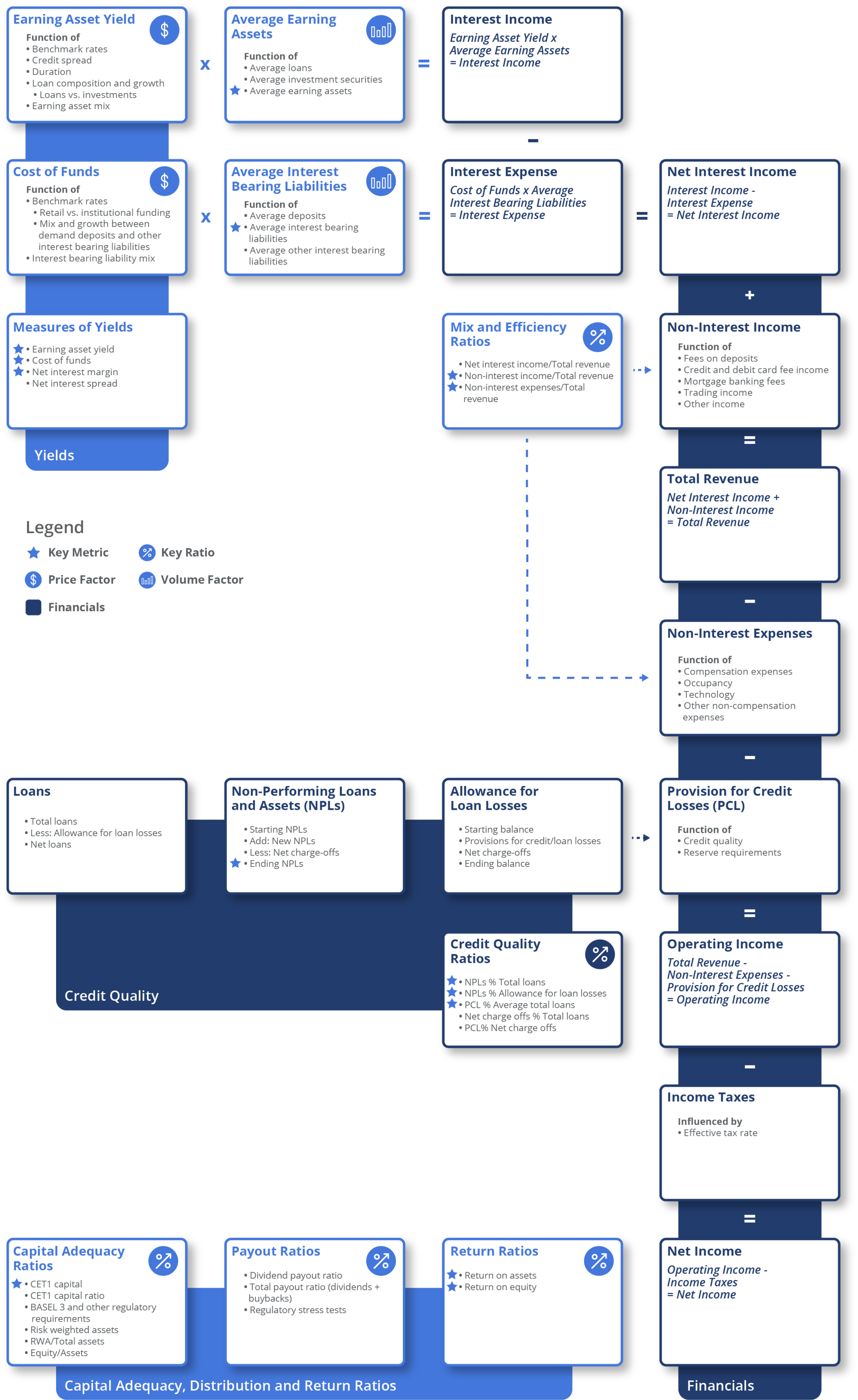
Earning asset yield isa measure of the interest yield generated by a bank’s interest-earning assets. It is defined as interest income divided by average earning assets.
Commercial Bank Business Model
SPREAD BUSINESS
Banks typically earn money by generating a spread between the price they pay for borrowed funds (deposits and other interest-bearing liabilities) and the yield generated when they invest those funds in loans and securities. Read More >
NON-INTEREST INCOME
In addition to the spread business, banks also generate fee income from services provided to their retail and corporate customers and fees charged for products like credit cards and deposit accounts. Large diversified banks may also offer investment banking, asset and wealth management, and other related services. Read More >
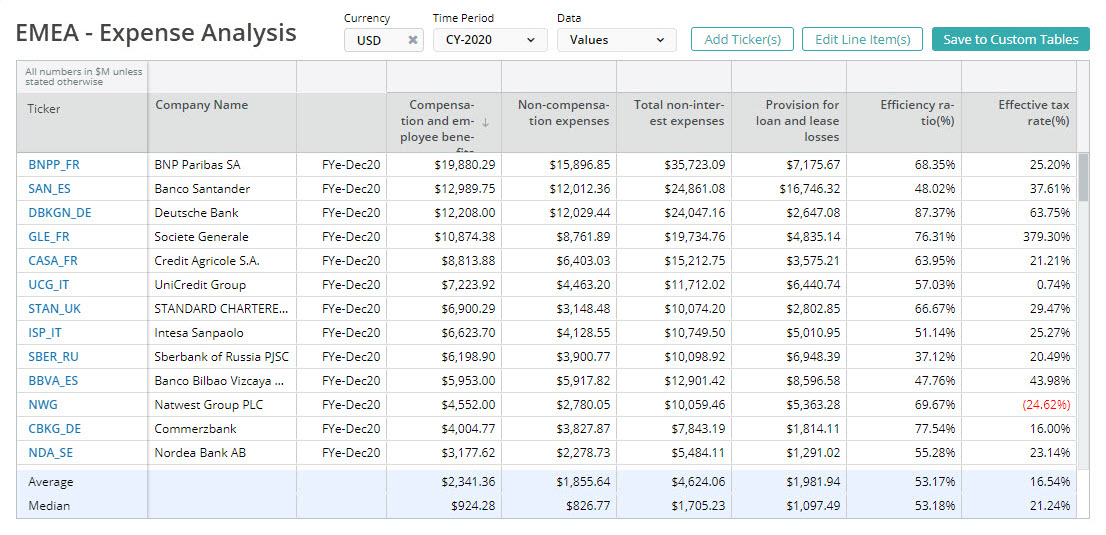
NON-INTEREST EXPENSES
Typically, compensation is the largest category of non-interest expenses. In addition to labor costs, banks also incur large expenses associated with their branch network (mainly traditional retail banks), technology infrastructure and processing costs. Read More >
CREDIT QUALITY
Management of credit risk is a crucial undertaking at banks. Underwriting credit includes an evaluation of the likelihood that a loan or an investment will not be repaid. Banks factor these costs into their pricing of credit by charging higher interest rates for riskier assets. Credit costs are also recognized as an expense in the income statement in the form of a provision for loan and credit losses. Read More >
BANK ACCOUNTING AND CREDIT QUALITY
To remove an impaired loan from the balance sheet, banks need to first recognize the loss as an expense. Income statement credit losses do not directly remove the loan, but instead increase the value of a contra-asset account called the allowance for loan losses. Loans are written off against these allowances (the term reserves is used in other geographies). Analysts will typically model the interplay of non-performing loans and the allowance for loan losses as follows:
| Non-Performing Loans (Asset) | Allowance for Loan Losses (Contra-Asset) | |
|---|---|---|
| Beginning of Period: | Non-Performing Loans | Allowance for Loan Losses |
| Plus: | New Non-Performing Loans | Provision for Loan and Lease Losses |
| Less: | Net Charge-offs | Net Charge-offs |
| End of Period: | Non-Performing Loans | Allowance for Loan Losses |
Impaired loans are removed by charging them off the balance sheet by using a previously established expense allowance. In the example above, a charge-off will reduce both the balance of non-performing loans as well as the allowance for loan losses.
CAPITAL ADEQUACY
As regulated entities, banks are required to maintain minimum capital standards, which impacts their ability to leverage their balance sheets. Higher capital requirements can decrease risk by requiring capital to absorb losses, but can also constrain asset growth and negatively impact profitability by making it more difficult to earn higher equity returns. Read More >
PROFITABILITY AND DISTRIBUTIONS
Analysts use asset and equity returns to evaluate and compare the profitability of banks. The two most commonly used measures of profitability are: Read More >
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the most important business metrics for a particular industry. When understanding market expectations for banking, whether at a company or industry level, here are some of the KPIs to consider:
Visible Alpha’s Standardized Industry Metrics
To understand market expectations for the commercial bank industry, a key information source is sell-side analyst estimate and consensus forecast data. The buy side, sell side and public companies leverage this type of data to conduct peer analysis, a type of analysis conducted by professional analysts that involves comparing standardized metrics of one company with those of similar companies. Because companies report metrics differently – and sometimes report on different metrics altogether – standardizing the key metrics for each company can be a cumbersome process.
Visible Alpha Insights includes analyst data, company data and industry data at level of granularity unparalleled in the market. Our industry data – Standardized Industry Metrics – enables market participants to quantify and compare market expectations for companies across 150+ industries.
Data as of January 2023
Industry KPI Terms & Definitions
Visible Alpha offers an innovative, integrated experience through real-time, granular consensus estimates and historical data created directly from the world’s leading equity analysts. Using a subset of the below KPIs, this data can help investors hone in on the key drivers of companies to uncover investment opportunities. Learn More >
Earning Asset Yield (EAY)
Earning asset yield isa measure of the interest yield generated by a bank’s interest-earning assets. It is defined as interest income divided by average earning assets.
Cost of Funds (COF)
Cost of funds is a measure of the cost of funding a bank’s interest-bearing liabilities. It is defined as interest expense divided by average interest bearing liabilities.
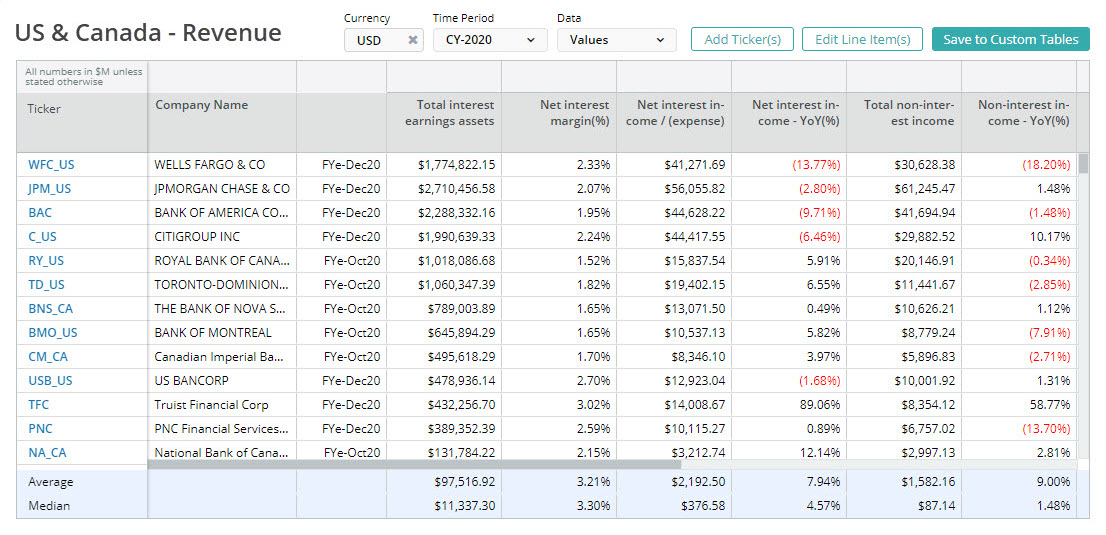
Net Interest Margin (NIM)
Net interest margin measures the net profitability of the bank’s spread business. It is defined as net interest income divided by average earning assets.
Average Earning Assets
Average earning assets generate interest income and are often calculated on a daily basis.
Average Interest Bearing Liabilities
Average interest bearing liabilities are the liabilities that incur interest expenses and are often measured on a daily basis.
Non-Interest Income/Total Revenue
Non-interest income/total revenue is the ratio of non-interest sources of income relative to total revenue.
Efficiency Ratio (Non-Interest Expenses/Total Revenue)
Efficiency ratio is the ratio of non-interest expenses relative to total revenue.
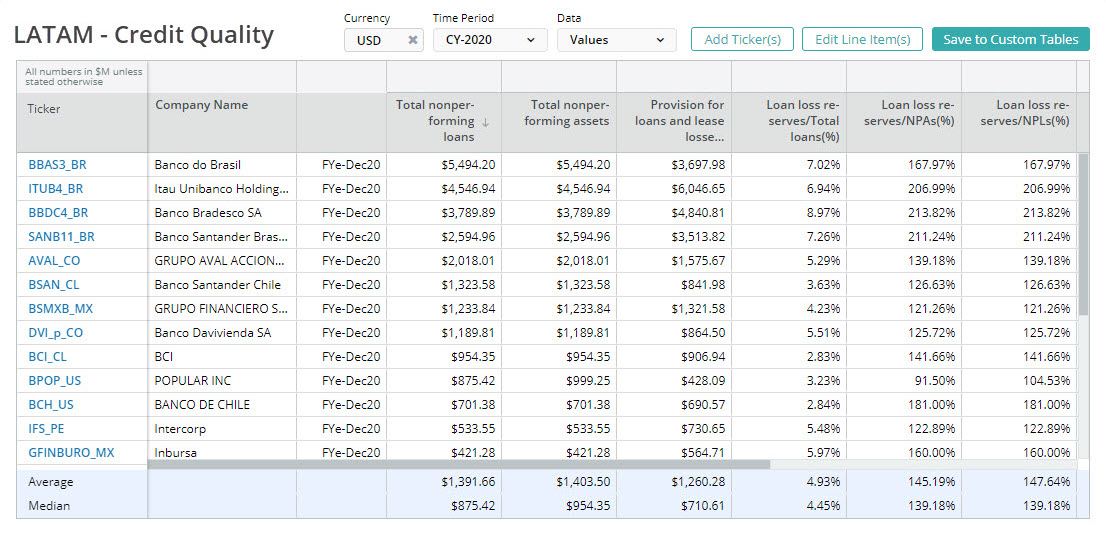
Non-Performing Loans
Non-performing loans are the loans classified as past due.
Non-Performing Loan Ratio
Non-performing loan ratio is an asset quality ratio that measures the relative prevalence of non-performing loans in the loan portfolio.
Coverage of Non-Performing Loans (NPLs % Allowance for Loan Losses)
Coverage of non-performing loans is a ratio that measures the level of reserves set aside for credit losses (NPLs).
Provisions for credit losses (PCL) % Average Total Loans
Provisions for credit losses is a measure of credit losses relative to the size of the loan portfolio.
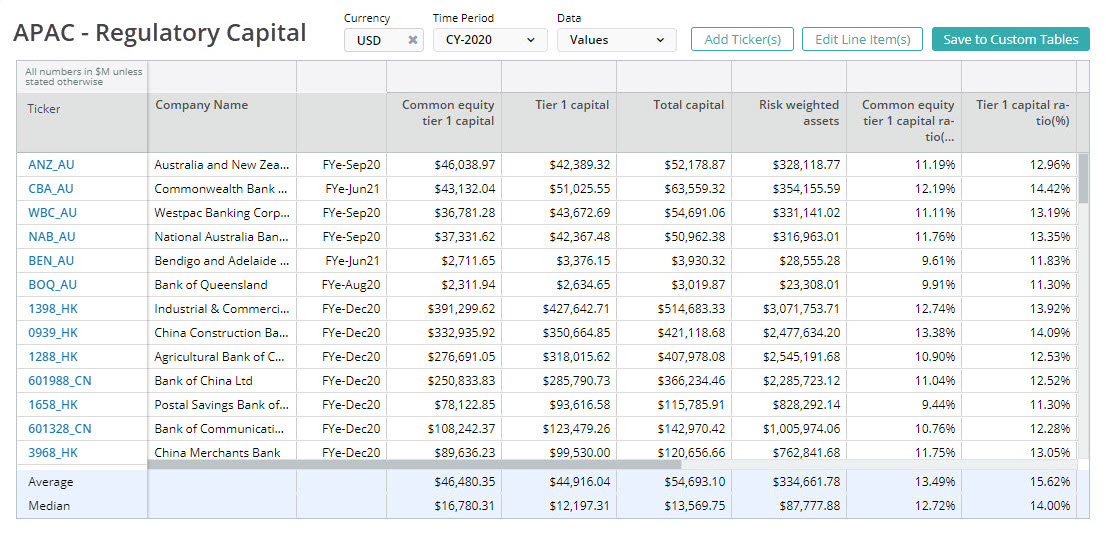
Common Equity Tier 1 Capital Ratio
Common equity tier 1 captial ratio is a regulatory ratio that measures the capital adequacy of a bank.
Download this guide as an ebook today:
Guide to Commercial Bank KPIs for Investment Professionals
This guide highlights the key performance indicators for the commercial banking industry and where investors should look to find an investment edge, including:
- Banking Industry Business Model & Diagram
- Key Commercial Banking Metrics PLUS Visible Alpha’s Standardized Industry Metrics
- Available Comp Tables
- Industry KPI Terms & Definitions