The Visible Alpha AI Monitor Update: What’s Next for AI?
The Visible Alpha AI Monitor aggregates publicly traded U.S. technology companies, providing a comprehensive measure of the current state and projected growth of the core AI industry. This encompasses the AI-exposed revenues for companies that are building AI infrastructure and capabilities for both enterprises and consumers.
Investors may use the Visible Alpha AI Monitor to generate new ideas to capture growth emanating from the core AI industry, as well as to evaluate the potential AI exposure of technology stocks in their existing portfolios. We have identified specific line items that capture potential growth of AI-related revenues that are available in the Visible Alpha Insights platform (see the goals, objectives, and methodology of the AI Monitor towards the bottom of this page).
Key Questions for 2025
|
Introduction: Agents?
The generative AI (GAI) trend gained momentum in 2023 as Cloud Service Providers invested heavily. In 2024, the GAI theme continued to evolve and gain momentum. Visible Alpha observed that companies attempted to make a greater push with GAI into their organizations with the hopes of improving efficiency and enhancing the client experience.
Over the past few years, we have seen a lot of innovation in the chip and model and that has benefited Nvidia. However, there has not been as much innovation at the application level to drive broader adoption of GAI with end users, leading to a more competitive business model. The verdict is still out on the magnitude of the productivity impact GAI may yield for businesses and individuals. Could these productivity benefits help to deliver stronger fundamentals and earnings growth, or will it be merely anecdotal?
This year looks poised to be the year of GAI adoption in enterprises with the integration of AI agents into role-specific workflows. AI agents seem to enable domain and persona-specific workflows to complement human roles in an organization. For example, a firm may have a unique AI agent for Research, Security, Analytics, Sales, and Customer Service to complement the human work done in these functions. We want to see how firms leverage these agents and what may be the direct or indirect impact on revenues and cost.
AI Agents
Visible Alpha AI Monitor Summary
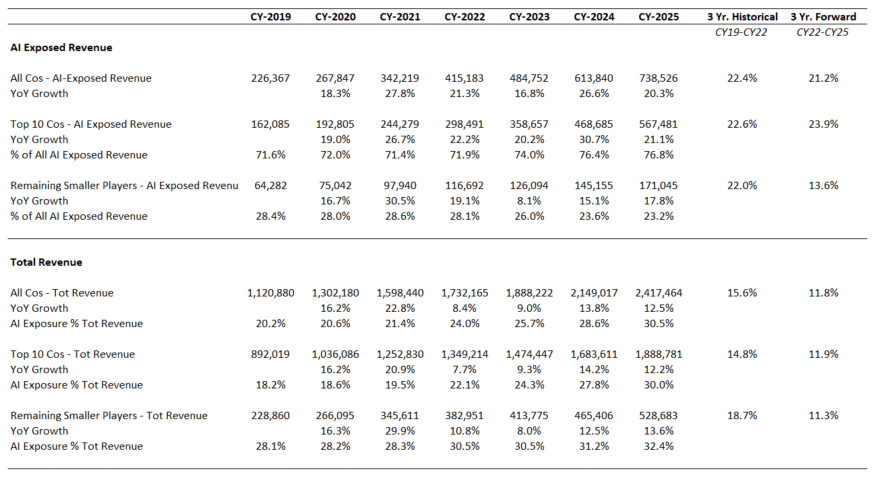
AI Growth and Performance Overview

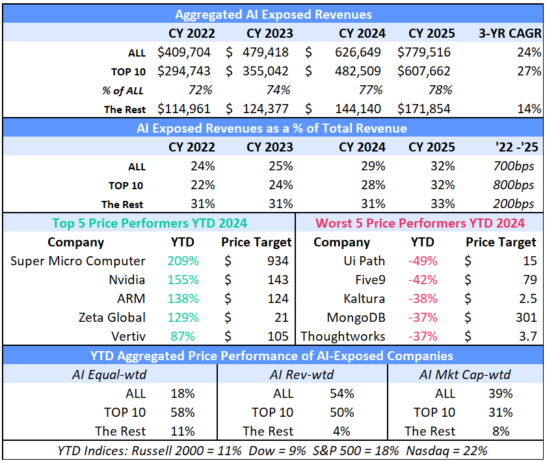
Source: Visible Alpha consensus (December 31, 2024). Stock price data courtesy of S&P Global. Current stock prices are as of the market close on December 31, 2024. TOP 10 = IBM, Qualcomm, Oracle, Microsoft, Intel, Amazon, Super Micro Computer, Dell, Nvidia, Google. These firms currently have the largest revenue-generating segments geared to AI.
2024 Performance Summary
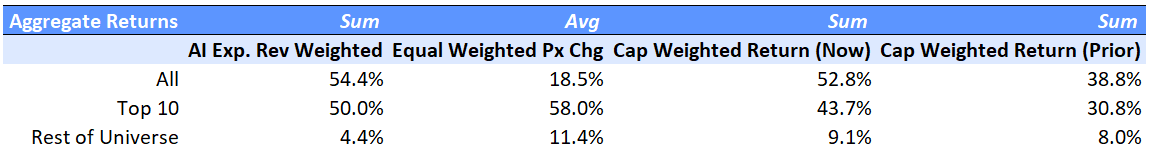
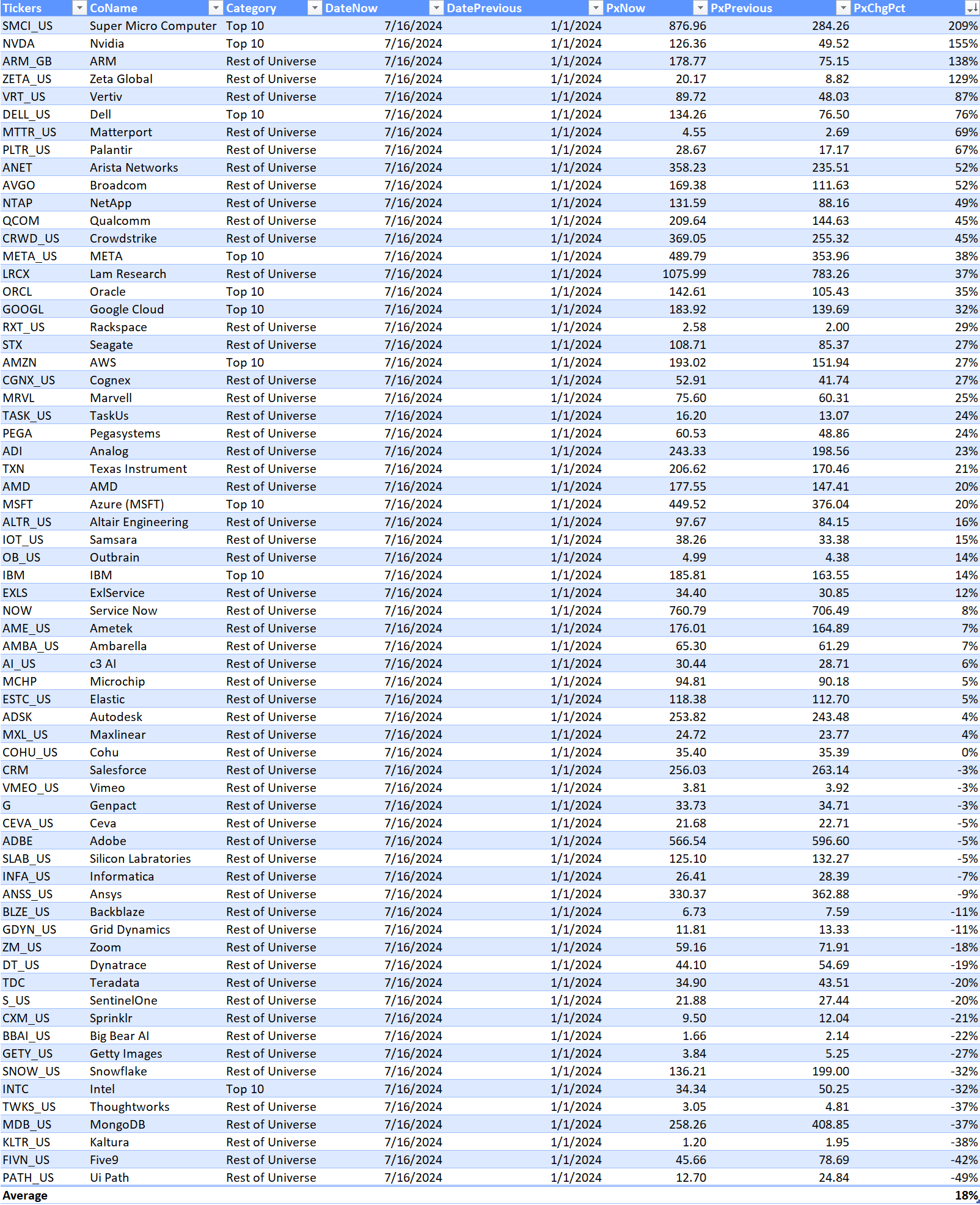
Currently, the Visible Alpha AI Monitor universe of 64 publicly traded U.S. companies is 79% weighted to the 10 largest companies, with the remaining 21% dispersed among 54 companies. On a market-cap-weighted and AI-exposed revenue-weighted basis, the Visible Alpha AI Monitor continued to be driven by stock price outperformance (vs. the S&P 500 index) of the largest companies this year. In addition, performance in the smaller companies (vs. the S&P 500 index), especially on an equal-weighted basis, lagged in the first half of the year, but in the second half picked up momentum. We noted this possible rotation in our July update: The Visible Alpha AI Monitor: Start of a Rotation?. On an equal-weighted basis, the AI Monitor generated an overall lower return when compared to the market-cap and AI-exposed revenue-weighted aggregations this year, driven by the drag of a lower return generated by the smallest names.
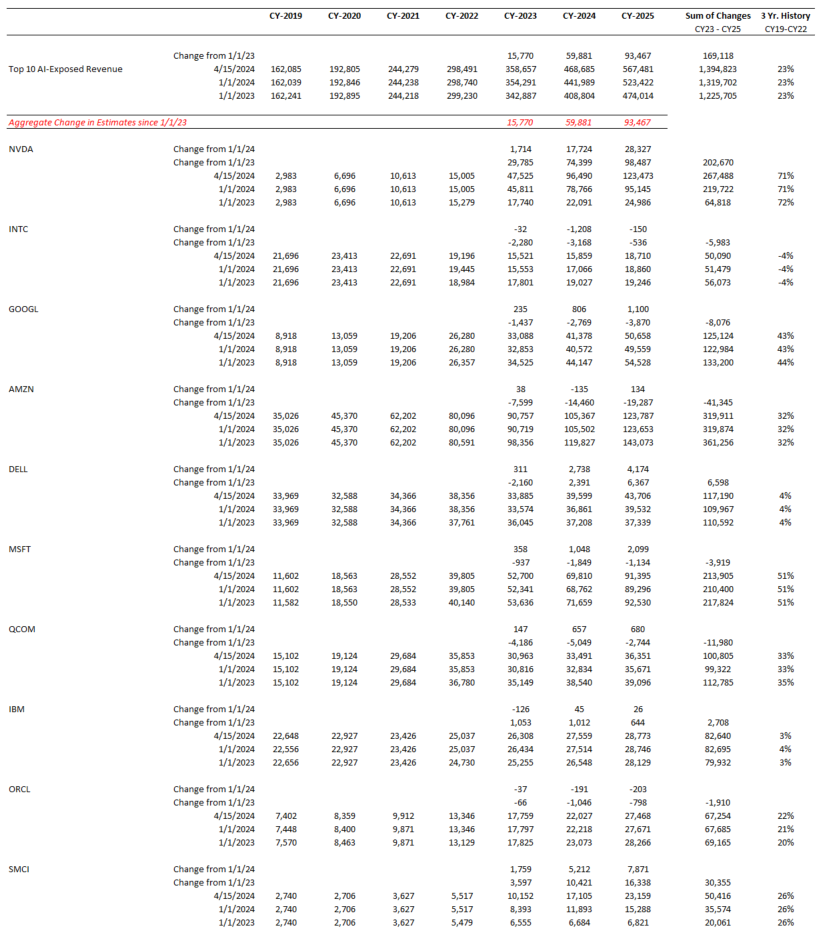
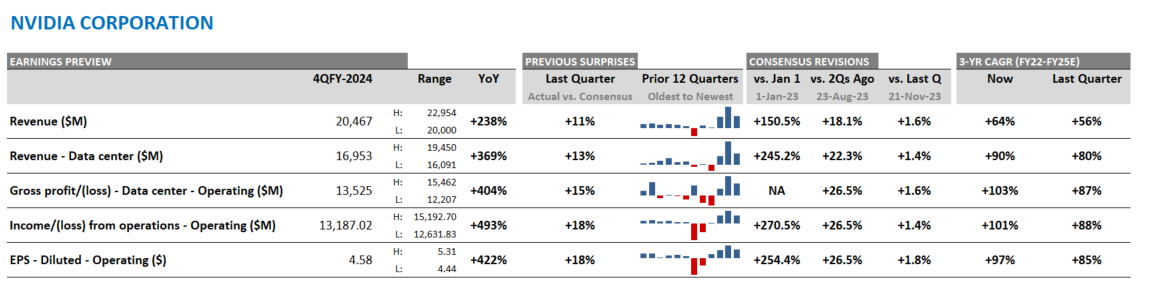
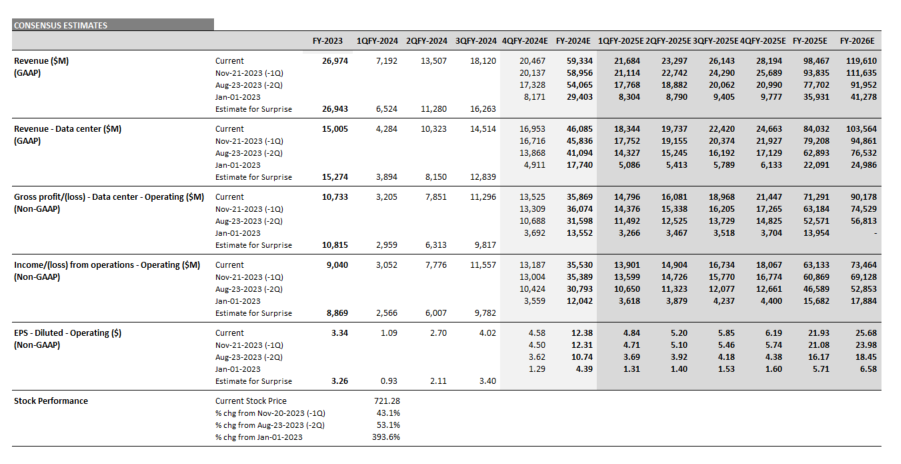
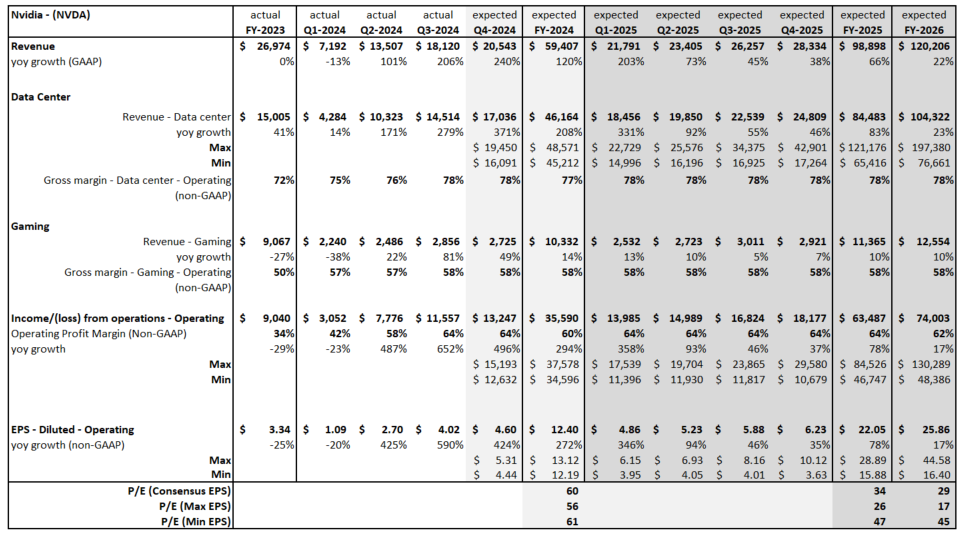
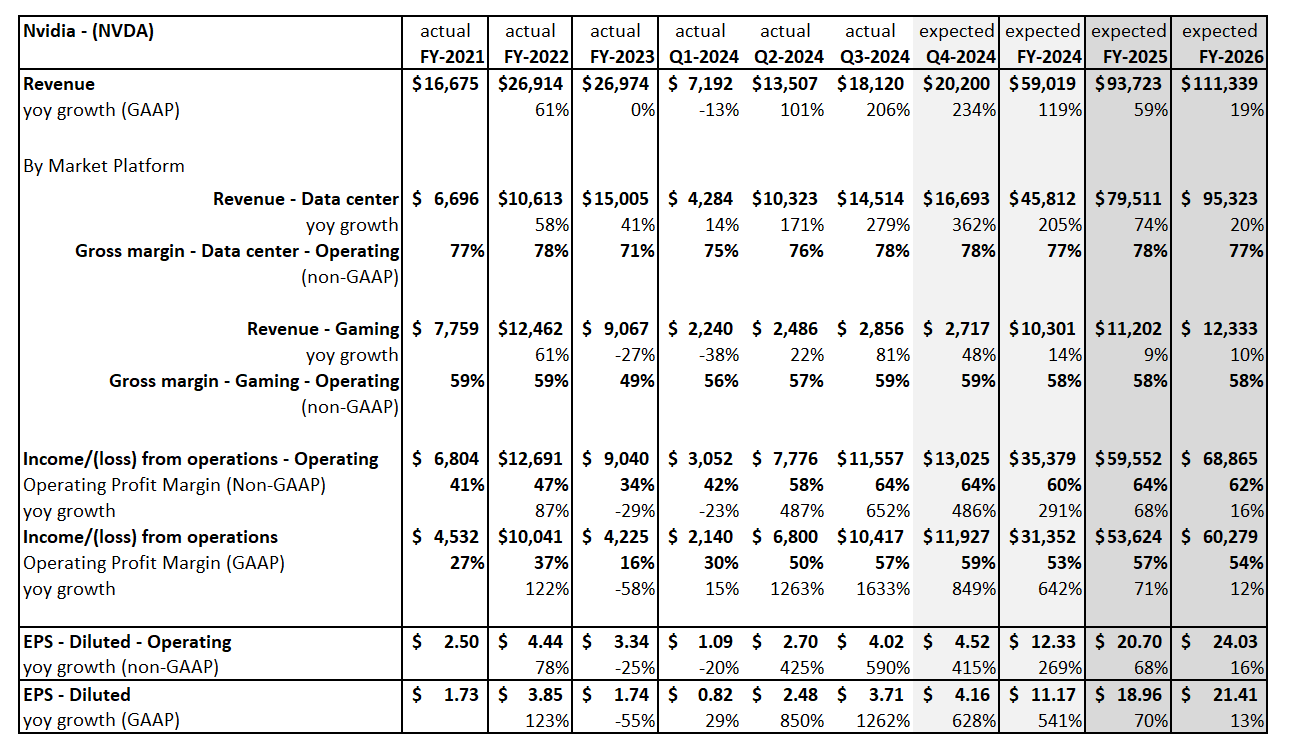
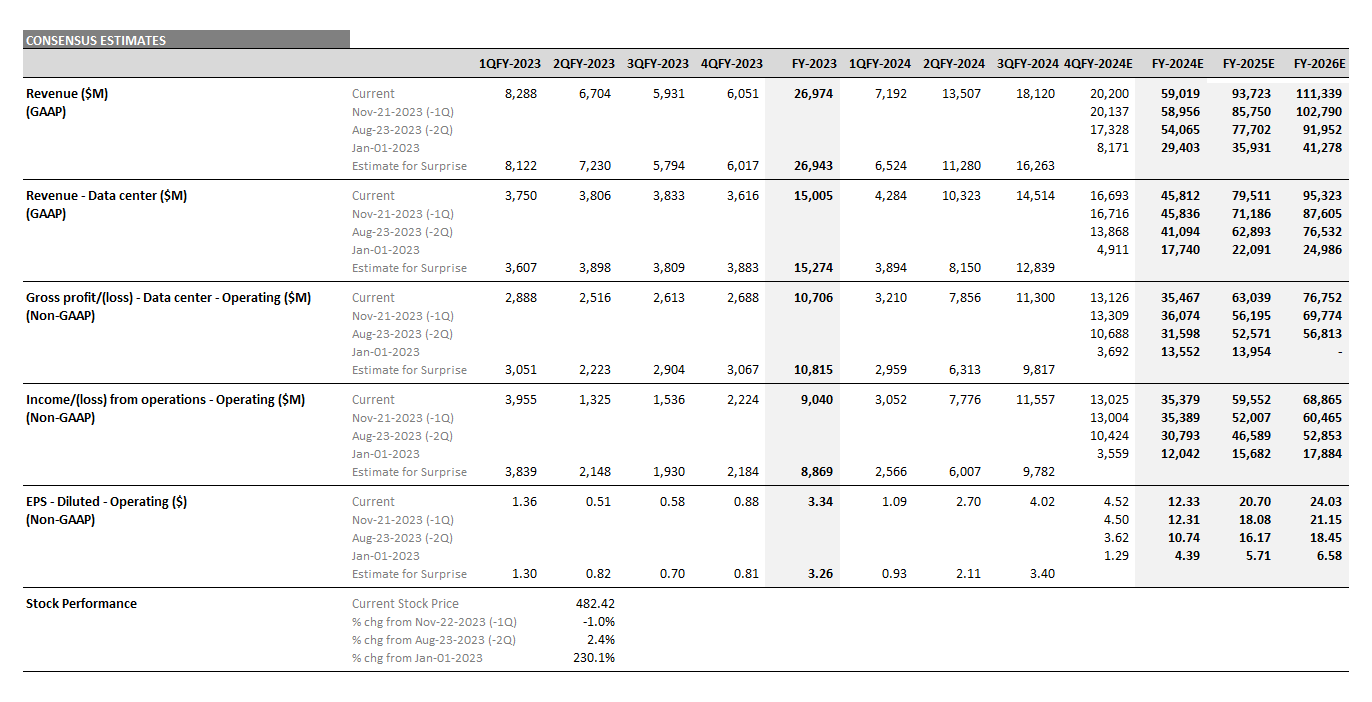
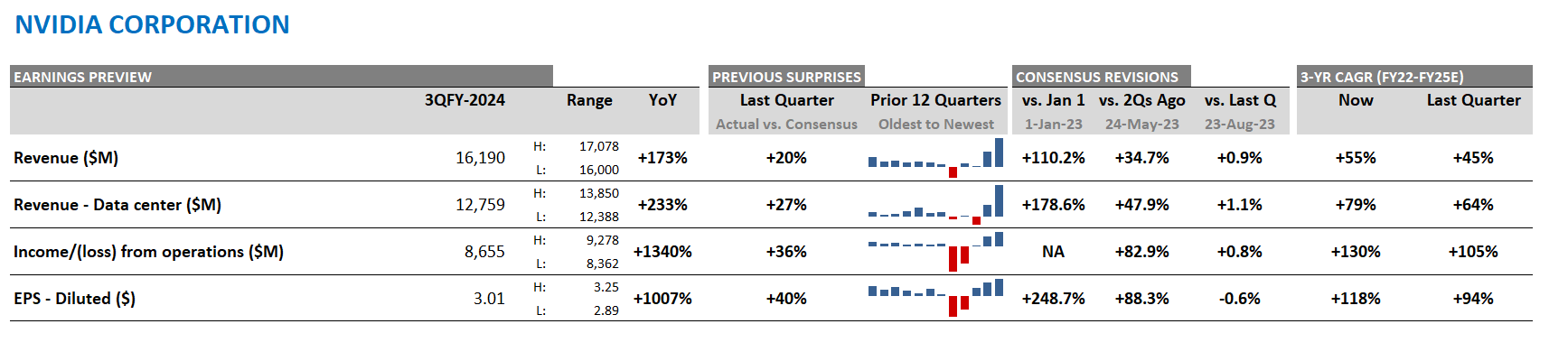
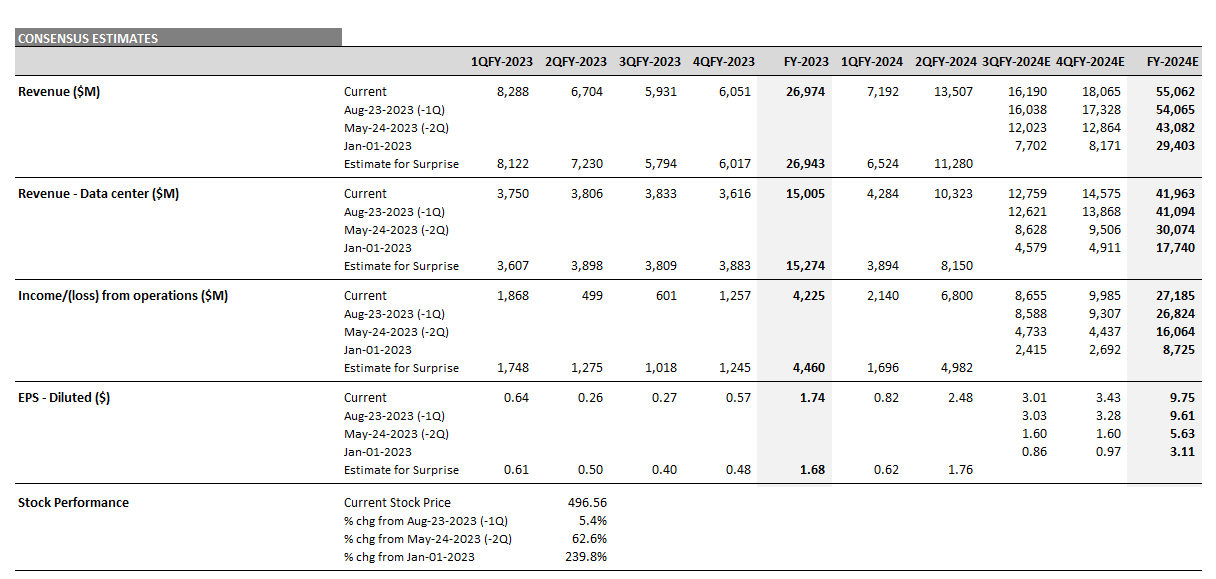
Top 10: Nvidia Continues to Dominate Expectations
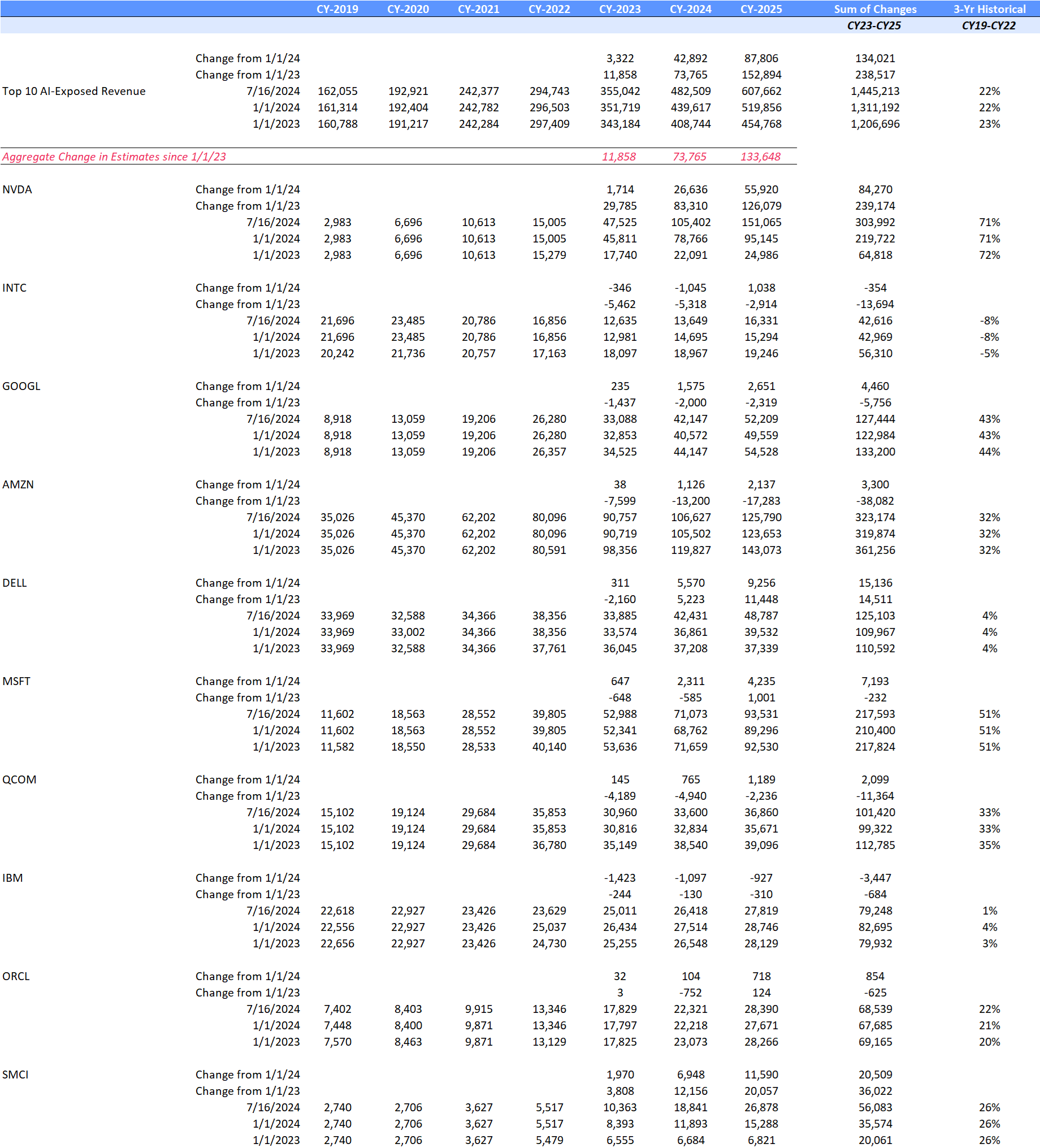
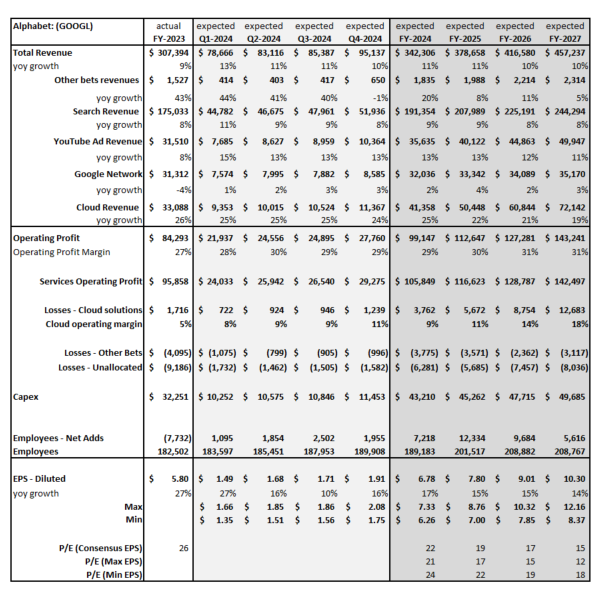
Based on an analysis of the 10 largest players, 2025 revenue forecasts for AI-exposed revenue segments increased $121 billion in total since January 2024. However, nearly $89 billion of the 2025 increase is from Nvidia, $10 billion from Super Micro Computer, and a further $12 billion increase from Dell. The declines in revenue estimates that the rest of the Top 10 has seen since January 2023 has largely stopped since the beginning of 2024. Lower expectations for AWS, Google Cloud, and Qualcomm QCT drove the downward revisions. However, the estimates for these companies have moderated and, in some cases, started to tick up, suggesting that the cuts to 2025 revenue expectations may have been too deep. Amazon and Alphabet now show upward revisions for 2025 and 2026
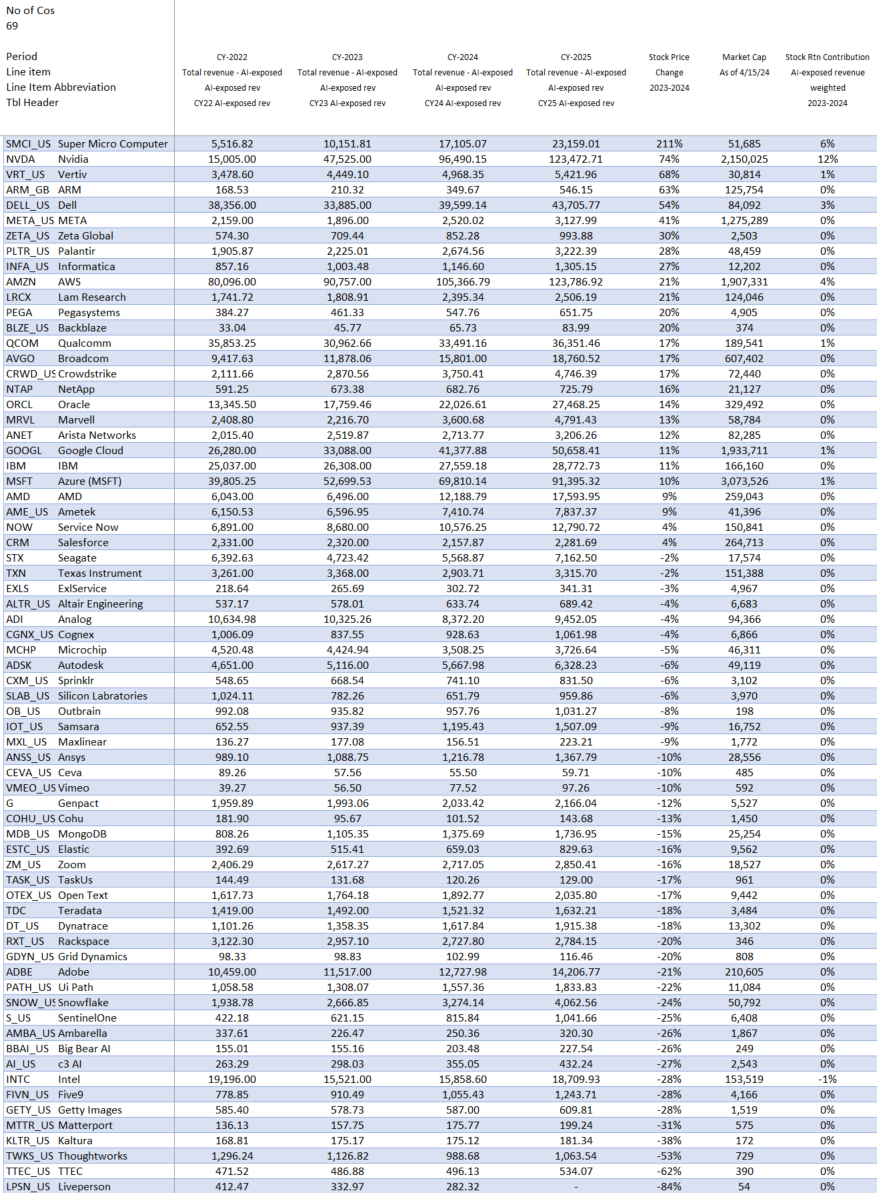
Smaller Contributors
The remaining list of 54 companies may serve as a good place for investors to discover new ideas by surfacing expanding new players. While smaller companies in aggregate have not performed as well as the Top 10, there have been some clear outperformers relative to the composite. Among the smaller firms, revenue growth expectations are very mixed. Strong double-digit revenue growth is expected at some firms, while others are seeing estimates decline. These dynamics may help investors identify emerging trends in the space.
In 2024, we have already seen that to be true with Pegasystems, Big Bear AI, and Arista Networks. These companies delivered strong outperformance (vs. the Russell 2000), which helped position these firms longer term as the possible up-and-comers in the space. Zeta Global, Vertiv, and Palantir are mid-caps with strong AI-exposed revenues and stock prices that also showed positive year-over-year outperformance.
In contrast to these small-cap and mid-cap outperformers, more than a third of the smaller companies in the AI Monitor substantially underperformed the Russell 2000 return of 11% in 2024. This weakness may imply that their fundamentals and valuations are under pressure. This weakness may make some of these companies go private or be attractive acquisition candidates. For example, Matterport, Alteryx, and Thoughtworks fell by more than 50%, and went private in 2024. These companies were removed from the AI Monitor.
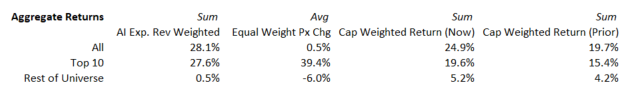
Performance: AI Monitor Aggregated Stock Return Breakdowns
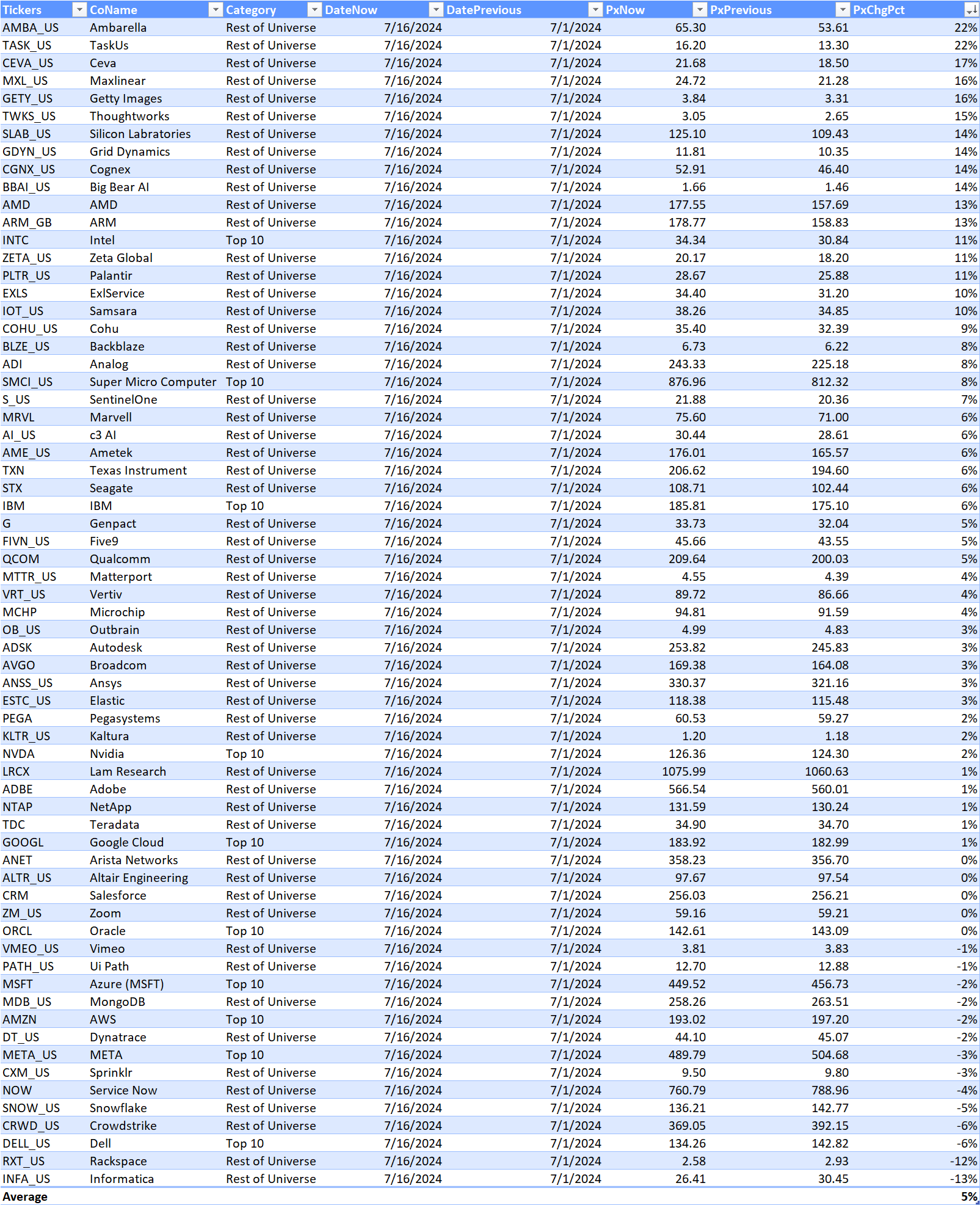
AI Monitor stock returns for the 64 companies are aggregated based on three weighting scenarios: weighted by the size of the AI-exposed revenues, equal-weighted and market cap weighted. Market cap-weighted returns show the direction of change year over year.
In CY2024 (as of 12/31/2024)
In Q2 (as of 7/17/2024)
In Q1 (as of 4/15/2024)

Source: Visible Alpha consensus (December 31, 2024). Stock price data courtesy of S&P Global. Current stock prices are as of the market close on December 31, 2024. TOP 10 = IBM, Qualcomm, Oracle, Microsoft, Intel, Amazon, Super Micro Computer, Dell, Nvidia, Google. These firms currently have the largest revenue-generating segments geared to AI.
2024 AI Monitor Detailed Breakdown

Source: Stock price data courtesy of S&P Global. 2025 Implied Return Data based on Visible Alpha target price consensus. Current stock prices are as of the market close on December 31, 2024.
What is Moving the AI Monitor
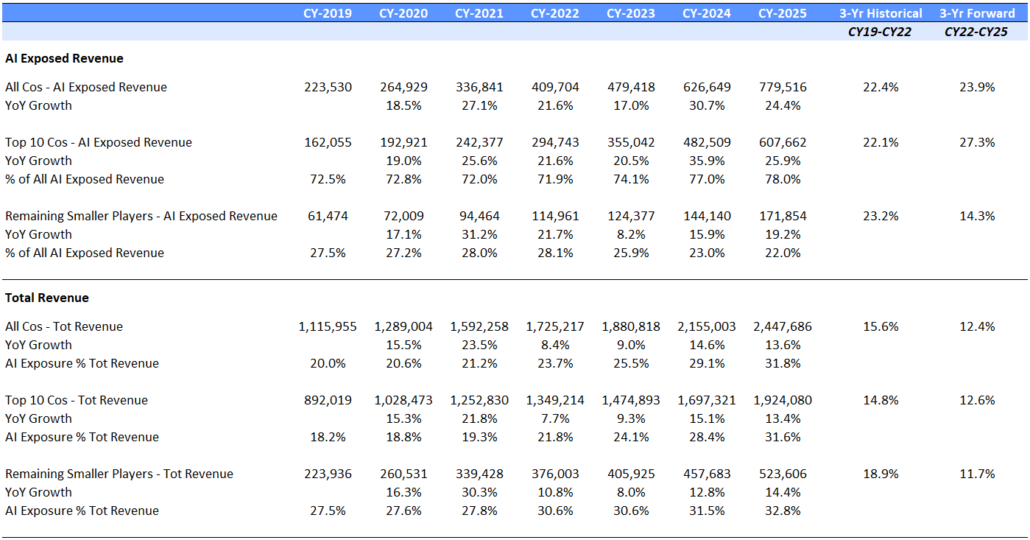
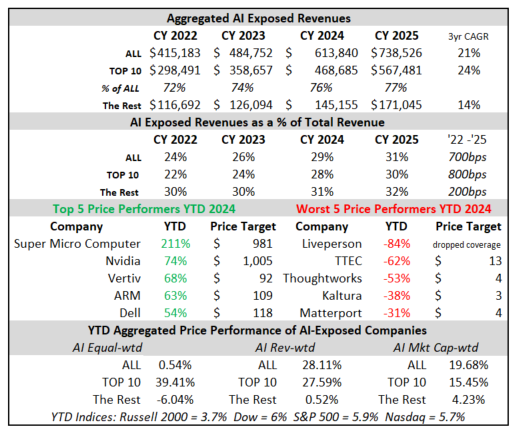
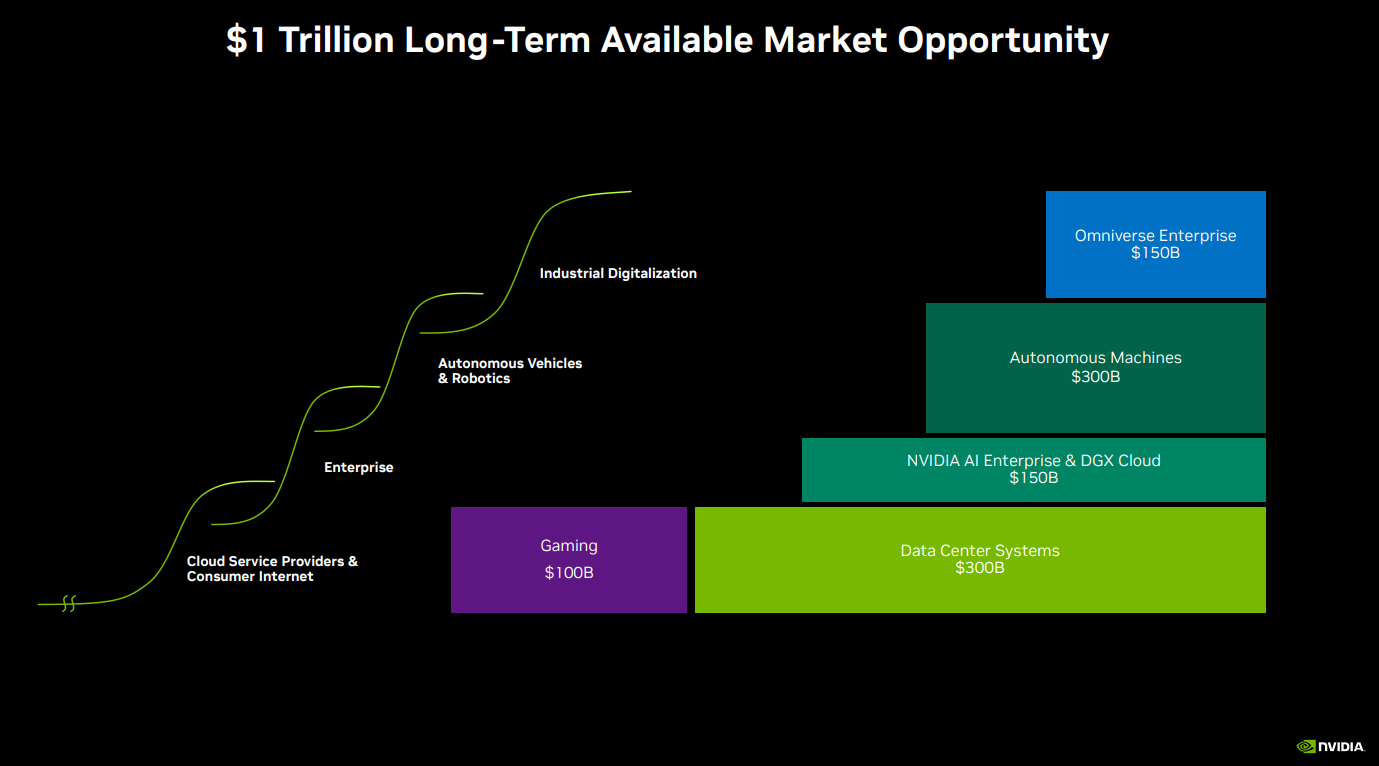
In 2024, seven out of the 10 largest AI-exposed revenue generators drove strong outperformance, while 40% of the smaller-cap AI stocks underperformed the small-cap index. AI-exposed revenues are expected to grow by close to $500 billion, from $475 billion at the end of 2023 to $971 billion at the end of 2026, driven overwhelmingly by the Top 10 largest companies in the AI Monitor with 23% coming from Nvidia alone.
AI-Exposed Revenue Aggregations

Source: Visible Alpha consensus (December 31, 2024). Stock price data courtesy of S&P Global. Current stock prices are as of the market close on December 31, 2024. TOP 10 = IBM, Qualcomm, Oracle, Microsoft, Intel, Amazon, Super Micro Computer, Dell, Nvidia, Google. These firms currently have the largest revenue-generating segments geared to AI
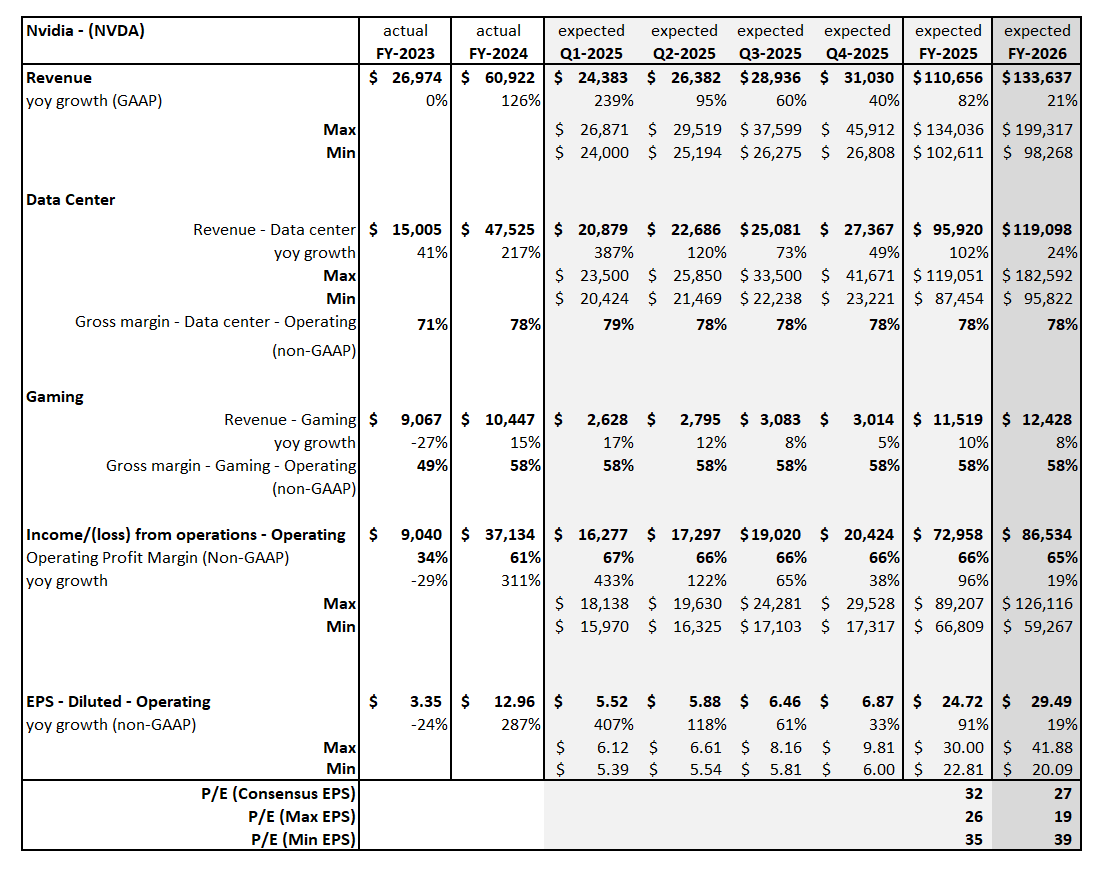
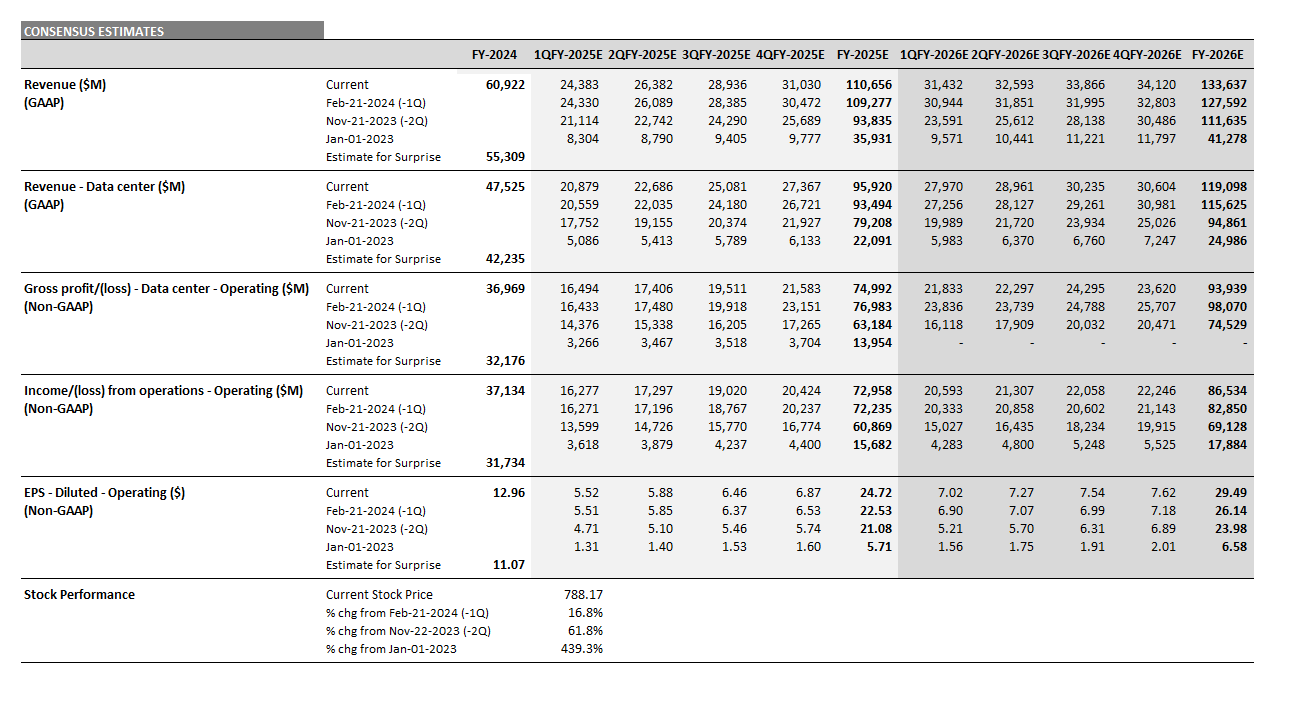
Nvidia’s Upward Revisions Continue
From the end of 2023 to the end of 2026, consensus expectations for Nvidia’s AI-exposed revenues were revised up by an incredible $443 billion. These upward revisions contributed significantly to both the AI-exposed revenue concentration and the stock performance of the AI Monitor.
In 2024, it is worth highlighting there was an additional $200 billion in upward revisions on top of the initial $200 billion made in 2023 to Nvidia’s Data Center revenue estimates. This optimism has been driven by continued heavy capex investment by the cloud service providers to support transforming data centers to accelerated computing to support AI applications. In 2025, upward revisions for Nvidia may increase further, but at a slower pace and smaller magnitude.
Dell, AWS and Google Cloud Expectations Gain Traction
Dell revenue estimates for the AI-exposed Infrastructure Solutions Group have come up nearly $30 billion for 2025 and 2026. This improved growth outlook is driven by AI servers and the potential for a replacement cycle fueled by must-have next-generation AI laptops. In addition, 2025 and 2026 Google Cloud and AWS estimates were revised up in 2024 by $26 billion, implying a more favorable outlook for those two AI-exposed businesses.
On the other hand, Microsoft’s Azure business has not moved much. However, it is important to highlight that Microsoft did recast the accounting of their segments and this impacted the Azure revenue line. In addition, the company created a new line called AI Services to showcase this emerging revenue line. In FY 2024, this business generated $4 billion. It is expected to ramp up growth and generate over $19 billion by the end of FY 2026, based on Visible Alpha consensus.
Super Micro Computer has seen significant volatility due to issues with its auditor. For 2025 and 2026, the AI-exposed revenue estimates have increased over $20 billion, as analysts gain more visibility into their growth. Given how rocky 2024 was for the company, it will be interesting to see how it performs in 2025.
What about Apple?
In addition to the Top 10, we are monitoring the potential AI revenue trends at Apple. The company released Apple Intelligence last summer and has embedded many new AI capabilities in its latest iPhone models. These product updates have not garnered much excitement with users and there are concerns that the new AI functionality has not been enough to make users want to upgrade their older phones. For 2025 iPhone units, expectations have come down from 237 million last year to now 225 million, in part due to lower growth in China. It will be interesting to see and hear what new updates Apple may reveal in 2025 that could get the market excited and fuel upgrades. For now, the verdict is still out on whether or not Apple Intelligence will drive the next iPhone upgrade cycle in 2025.
AI-Exposed Revenue Revisions Summary

Source: Visible Alpha consensus (December 31, 2024). Stock price data courtesy of S&P Global. Current stock prices are as of the market close on December 31, 2024. TOP 10 = IBM, Qualcomm, Oracle, Microsoft, Intel, Amazon, Super Micro Computer, Dell, Nvidia, Google. These firms currently have the largest revenue-generating segments geared to AI.
Regulatory Backdrop: Changing of the Guard and Stargate
Under the new US administration, President Trump wasted no time. He is focusing on securing AI leadership for the US. The rhetoric around regulation, governance, and oversight of AI has been silenced for now as he moves quickly to establish new AI infrastructure initiatives in the US.
Trump launched the Stargate Project, an AI infrastructure company that plans to invest $500 billion over the next four years to build out new AI infrastructure in the United States. Stargate will be initially financed by SoftBank, OpenAI (Microsoft), Oracle, and MGX. Speaking with President Trump, Oracle CTO, Larry Ellison, Softbank CEO, Masayoshi Son, and OpenAI CEO, Sam Altman, outlined the ambitious goals of Stargate and their initial commitment of $100 billion and the subsequent $400 billion of financing over the next four years.
According to the press release, SoftBank and OpenAI are the lead partners for Stargate, with SoftBank having financial responsibility and OpenAI having operational responsibility. Masayoshi Son will be the chairman. Arm, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Oracle, and OpenAI are the key initial technology partners. The buildout is currently underway, starting in Texas. As part of Stargate, Oracle, NVIDIA, and OpenAI will closely collaborate to build and operate this computing system.
There is currently some debate in the market about how Stargate will be financed. Based on comments from CEO Satya Nadella, Microsoft has already committed to investing $80 billion in AI data centers this year. Given Microsoft’s commitment, Softbank may contribute an additional $20 billion to complete the initial $100 billion of investment for Stargate. There has been some skepticism about whether or not Softbank has the funds secured for future investment.
Based on Visible Alpha consensus this fiscal year, Softbank is expected to have $40 billion in cash and $78 billion in long-term debt on its balance sheet. Additionally, Softbank’s monetization of gains from its early investment in Alibaba may help to finance some of the investment in Stargate. Based on Alibaba’s May 2024 20-F, Softbank owned a 14.2% stake in the stock. According to a Softbank press release from Softbank (Recognition of Gain on Sale of Investment Securities in Non-Consolidated Financial Results Following Completion of Settlement of Alibaba Prepaid Forward Contracts | SoftBank Group Corp.), the position has largely been monetized through forward contracts and a gain booked. The exact numbers will not be clear until the release of the 2024 20-F in May 2025.
Stargate: $500 Billion AI Infrastructure Project
In 2023, President Biden issued an Executive Order to “ensure that America leads the way in seizing the promise and managing the risks of artificial intelligence (AI)” and 25 new regulations around AI were passed. The Order contained initiatives to strengthen AI safety and security, privacy protections, innovation, and competition, along with supporting consumers, workers, and equity. In January 2024, the agencies completed more than two dozen activities around AI talent, risks, and implications for the U.S. In addition, the White House created a blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (ai.gov). However, this order, the AI Bill of Rights, and the progress made are no longer available on the ai.gov site, suggesting a complete change in direction.
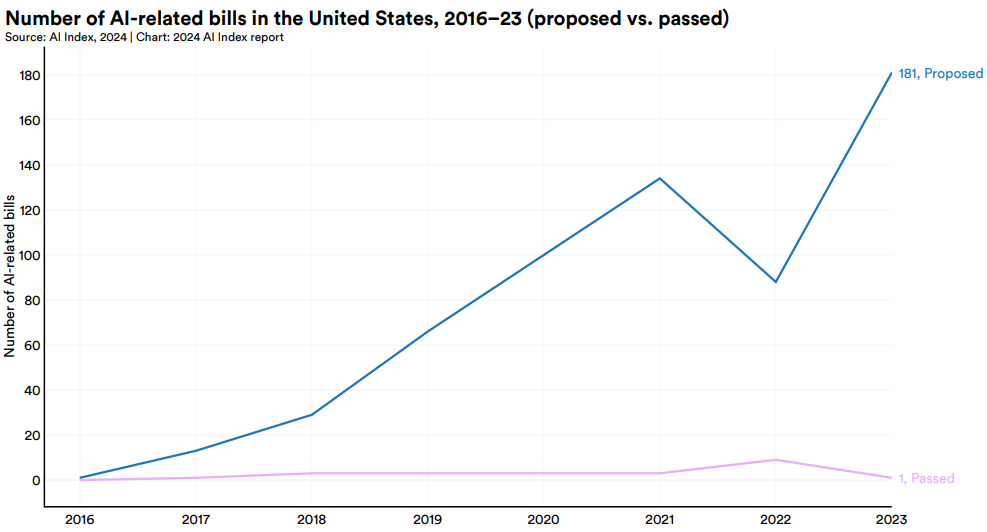
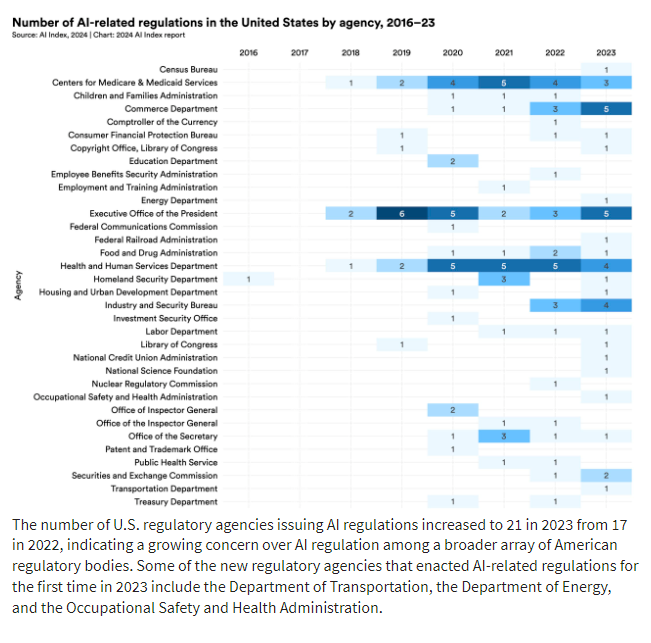
As the government continues to focus on AI and its implications for the U.S., the new administration seems to be more focused on building and securing the infrastructure, instead of trying to regulate AI. Stanford University released an update in April 2024 to its AI Index. At that time, there was a surge in proposed bills for 2024-2025. The trajectory of the proposed regulations suggested we could see more regulations in 2025. However, given the changes this week, these proposals may be scrapped, delayed, or changed.
Biden’s AI Executive Already Removed

Source: Administration Actions on AI – AI.gov, January 22, 2025.
Passed AI-Related Regulations in the US and EU

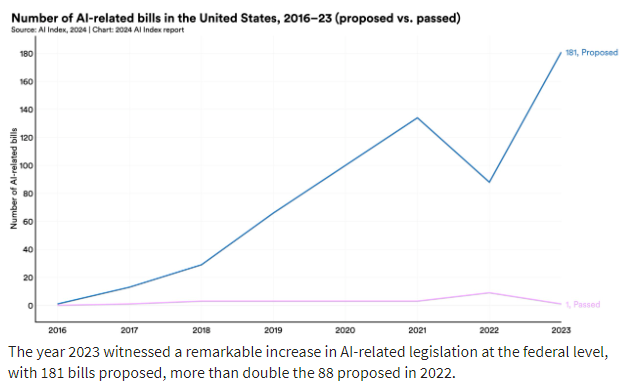
The number of AI-related regulations has risen significantly, both in the past year and over the last five years (Figure 7.4.1). In 2023, there were 25 AI-related regulations, a stark increase from just one in 2016. Last year alone, the total number of AI-related regulations grew by 56.3%. Source: Stanford University AI Index 2024 (https://aiindex.stanford.edu/report/)

In 2023, policymakers on both sides of the Atlantic put forth substantial proposals for advancing AI regulation The European Union reached a deal on the terms of the AI Act, a landmark piece of legislation enacted in 2024. Meanwhile, President Biden signed an Executive Order on AI, the most notable AI policy initiative in the United States that year. Source: Stanford University AI Index 2024 (https://aiindex.stanford.edu/report/)
Final Thoughts
Given Trump’s support of AI and the expansion of AI infrastructure in the US, cloud service providers (CSPs) will continue to remain front and center. In 2024, Nvidia and Palantir led once again, driven by strong demand for AI infrastructure solutions. Will this continue again in 2025?
At the same time, debates are emerging about how best to create scalable enterprise applications for GAI. For many firms, it is not clear how they will participate in bringing GAI to enterprises and grow the impact of AI exposure in their business models. The importance of specializing and bringing domain expertise to smaller models will be increasingly critical to the success of these tools. In 2025, we are watching the pace at which companies will be enabling innovation with AI in enterprises. There is some skepticism emerging about the actual use cases, real impact, and ROI. AI agents and AI laptops may be compelling mechanisms for fostering broader adoption and driving specialized applications in enterprises. However, the verdict on these new AI tools is still out.
We are interested to see how the Stargate project partnership between ARM, Nvidia, Oracle, Softbank, and OpenAI (Microsoft) could drive growth in sales and earnings in the key players. There may be a few new companies in the AI space that emerge as significant beneficiaries of the significant AI infrastructure growth in the US. At the moment, it feels like 2025 could be a rising tide that lifts all boats.
AI Monitor Goals and ObjectivesThe objective of the Visible Alpha AI Monitor is to show the investment community which companies are likely to drive AI going forward. As the world embraces AI and its applications to enterprise workflows and our daily lives, big questions exist about how AI’s impact on company business models will unfold over the next 3-5 years. AI can potentially free people from tedious grunt work to enable more focus on critical workflows that require human creativity and analysis. A primary goal of the Visible Alpha AI Monitor is to show which U.S. companies and specific line items we are keeping an eye on as the embryonic AI theme emerges across company fundamentals and begins to scale broadly across the economy. We are monitoring how AI may be reflected in the numbers and which companies may be benefitting more or less. This universe attempts to be comprehensive and to show investors the dynamics of both the large and smaller U.S. players. Additionally, it aims to help investors identify new names that may be smaller and less covered but potentially growing and emerging more quickly. AI Monitor MethodologyUsing Visible Alpha’s comprehensive database of detailed estimates pulled directly from sell-side analysts’ spreadsheet models, we have assembled an aggregation with a universe of 64 publicly traded companies that are contributing to the infrastructure and broad scaling of AI capabilities. This monitor aims to provide a current and future snapshot as to where AI-related revenues are and is not growing across each of these 69 companies, particularly the 10 largest. The AI Monitor provides three measures of stock performance for its universe. These metrics are meant to show the returns of various weighting schemes. The returns are calculated on both an equal-weighted and market-cap-weighted basis. The universe performance of the AI Monitor is also weighted based on AI-exposed revenues and calculated in aggregate. From 2024, the return calculations were standardized, and market-cap-weighted now reflects year-over-year changes. For Visible Alpha subscribers, details of these companies can all be found within the Visible Alpha Insights platform. Each company included in the monitor has coverage by at least four sell-side analysts. In addition, given the quickly evolving state of the AI space, these line items are subject to change and may shift significantly over time. We plan to refresh the data on an ongoing basis and provide regular updates. |